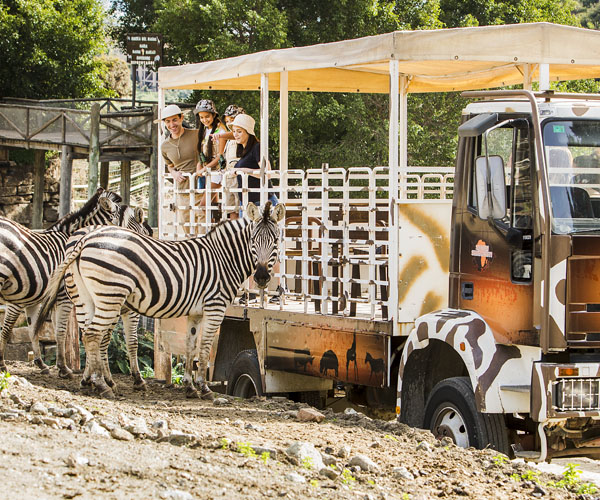
If you come in costume, you get free admission! Get it here.





Emperor marmoset