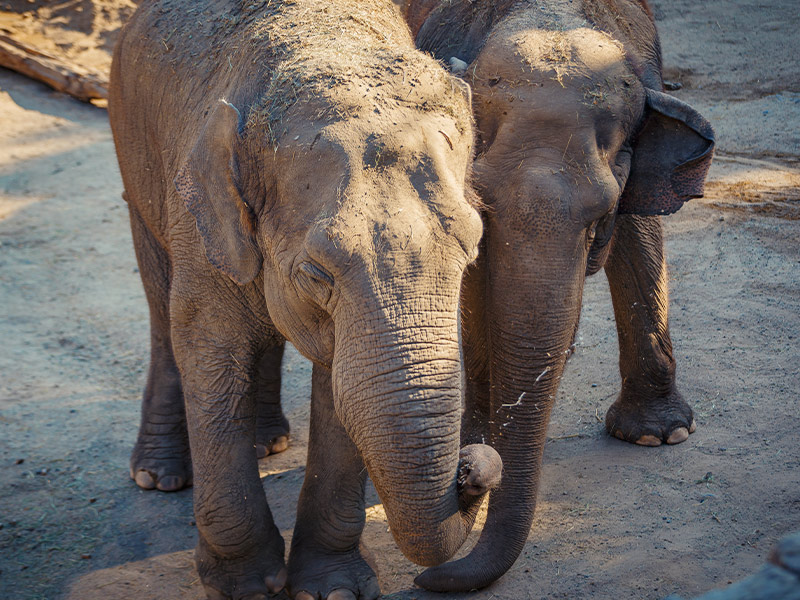
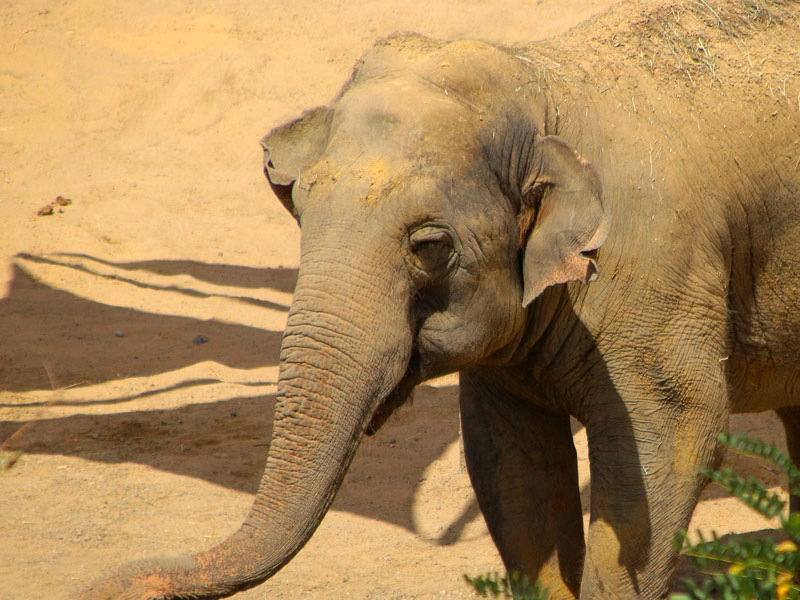
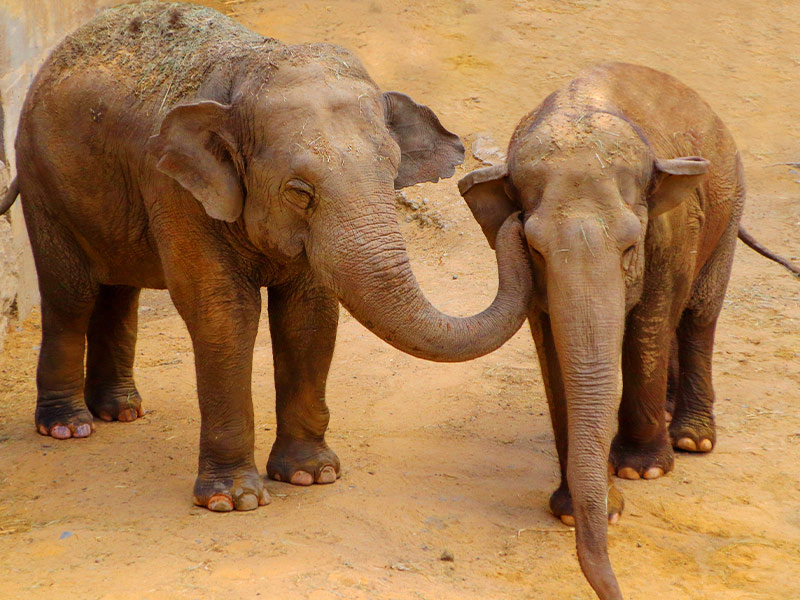
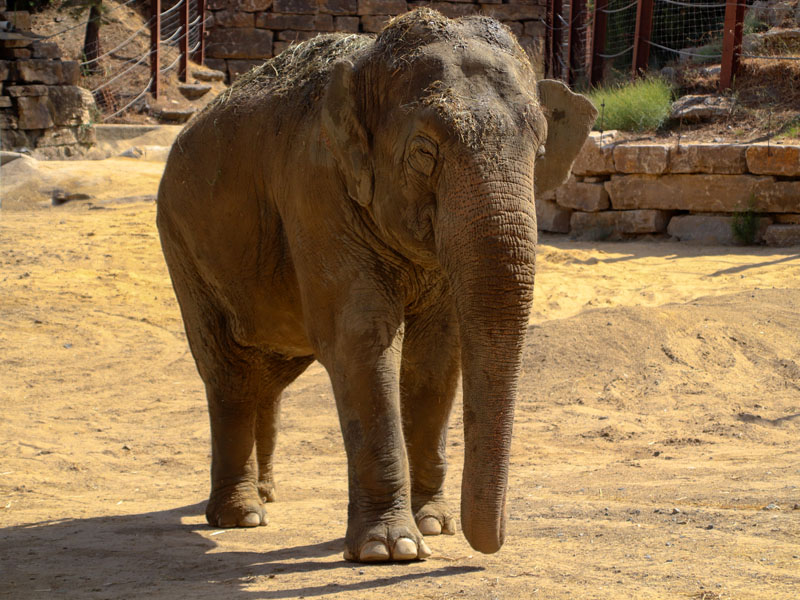
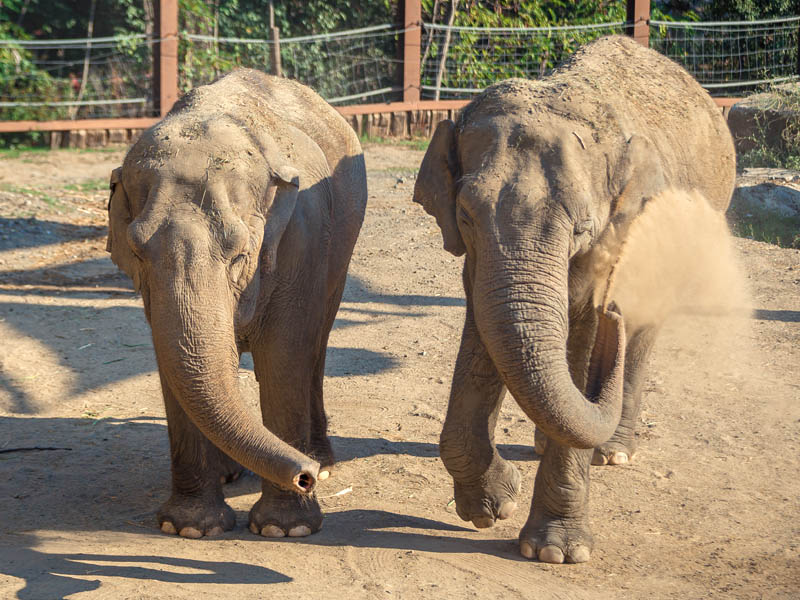
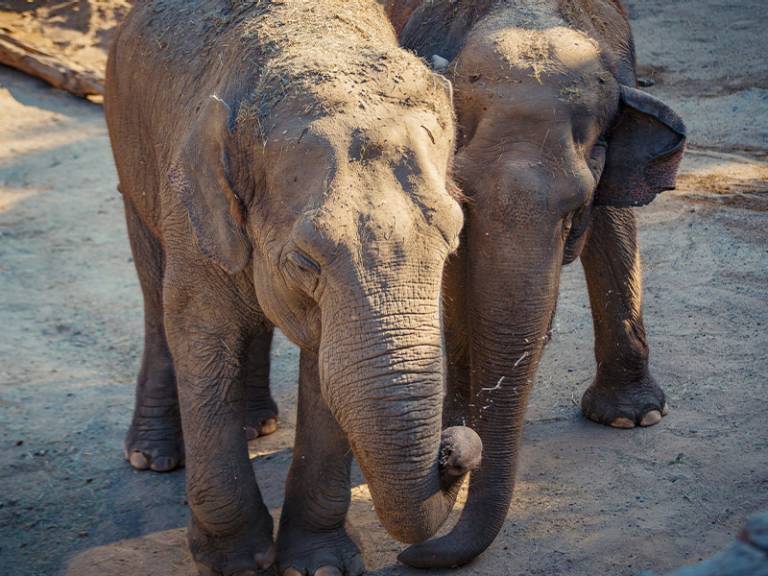
It is widespread in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia.
There is a clear sexual dimorphism, the male is much larger than the female and they have tusks while females lack them.
The group has a matriarchal social organization. Females and offspring live together in a group, while males live in smaller groups or alone. The female will only allow the strongest male to mate with her, will give birth to a calf after 18 to 23 months of gestation and will nurse it for 2 years. This causes reproduction to occur every 4-5 years.
Differences between the Asian and African elephant:
- The size, the Asian elephant is smaller than the African.
- Only the male of the Asian species has tusks, but in the African species both males and females have them.
- The Asian has a single extension at the tip of its trunk while the African has two extensions.
- The Asian's ears are smaller and rounder than the African's.
- Asian elephants have four hooves on the hind leg while African elephants have only three hooves.
- Elephas maximus has a flat back while Loxodonta has a sloping back.
The Asian elephant has several behaviors related to thermoregulation. During the hottest hours of the day, they are less active and spend time in shaded areas, bathe frequently, use their trunks to spray water or saliva on themselves, cover themselves with mud or dirt to keep their skin cool and wiggle their ears to remove excess heat.
The biggest threats to E. maximus include habitat loss and fragmentation due to the growing human population and the poaching of male elephants for their tusks.
The Selwo Aventura group is part of the European Endangered Species Program (EEP) of the European Association of Zoos and Aquaria (EAZA).