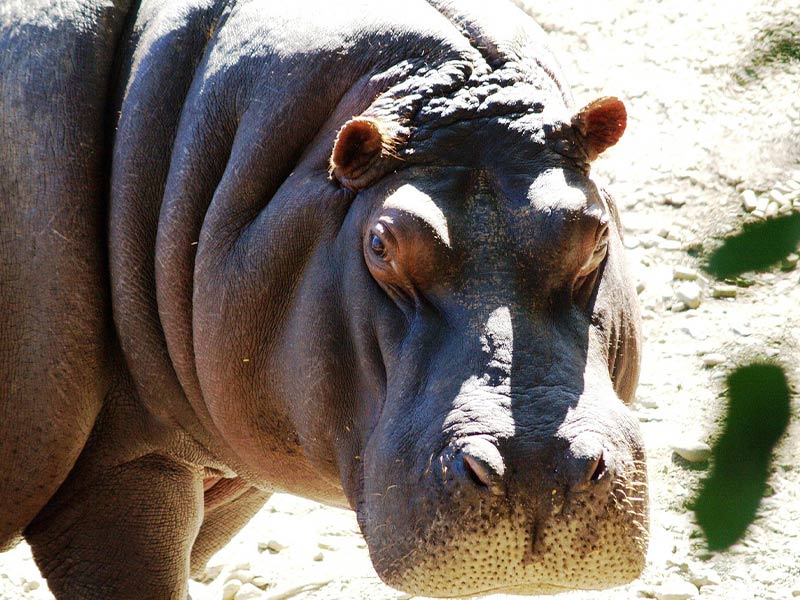
Hippopotamuses are found in the rivers of the African savanna and the major rivers of Central Africa. It is a semi-aquatic mammal that usually inhabits lakes, rivers and swamps deep enough to submerge its entire body.
The hippopotamus lacks sweat and scent glands. Instead, the mucous glands secrete a thick oily layer of red pigmented fluid, this fluid is a combination of hypposudoric acid and norhipposudoric acid that create a sunscreen effect by absorbing the sun's ultraviolet rays and prevent the growth of disease-causing bacteria.
On land, they can move at speeds of up to 30 km per hour. In shallow water, their short legs provide powerful propulsion through the water, while their webbed feet allow them to navigate shallow river bottoms.
It is a very social species, living in groups of approximately 20 to 100 individuals. It leads a very sedentary life, resting most of the day and leaving its resting pools in the evening to feed. Most of its activity is nocturnal and females are the leaders of the herd.
They mate and give birth in the water to a single calf after eight months of gestation. During pregnancy, the female is isolated from the group until 14 days after birth when she rejoins the group. It can be very protective and aggressive.
The hippopotamus is threatened because of habitat loss and poaching for its meat and ivory for its canine teeth, even though hunting this species is illegal.